Financial institutions globally must comply with their local regulatory framework. In the European Union they must comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), while companies in the US must adhere to the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) regulations.
The regulatory landscape poses a unique challenge for their archiving solutions of main vendors such as Global Relay and Smarsh. Being based in the United States, they are obligated to adhere to U.S. regulations requiring the archiving of all financial data. However, the GDPR prohibits non-European countries from accessing European data.
In this blog post, we’ll break down these difficulties and present AGAT’s effective solution to address the problem.
US vs. GDPR Data Archiving Requirements
In the United States, financial institutions have a responsibility to be transparent and accountable by saving electronic data. This ensures a reliable financial system that protects investors and follows regulations like those set by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA).
At the same time, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) created by the European Union (EU) aims to safeguard personal data. It focuses on privacy and security in our interconnected world. GDPR empowers individuals to control their personal information and sets strict rules for its use, storage, and sharing.
The Challenge of Archiving EU Data
Complying with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) can pose complexities for these US vendors as it requires storing data exclusively within the EU or in jurisdictions that provide adequate data protection levels.
A significant development was the invalidation of the EU/US Privacy Shield by the Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU) in the Facebook Ireland v Schrems (Schrems II) case. This highlighted the divergence in data protection approaches between the US and the EU, potentially exposing EU personal data to inadequate protection due to potential US government access.
The problem is generated when companies that have both American and European branches, like banks, investment funds or insurance companies, archive their data on popular platforms like Smarsh or Global Relay.
The nature of these companies being located in the US and thus, allowing non-european agents to have access to EU based sensitive data, signifies a violation of the GDPR data-privacy laws.
The Solution: AGAT SphereShield’s Archive and eDiscovery for Microsoft Teams
AGAT offers a unique solution that surpasses the limitations of US vendors by providing an on-premise approach.
With AGAT’s Archive and eDiscovery, data can be archived on local servers or VPS, which means that all the PII or other sensitive information stays within the borders of the GDPR jurisdiction.
As a result, European financial institutions or US companies with EU branches can achieve compliance with both US regulations and GDPR while maintaining full control over the data transfer process.
What is more, AGAT’s eDiscovery has the unique functions to search by both written and oral conversations through multiple parameters like participants, channels, text, dates and more.
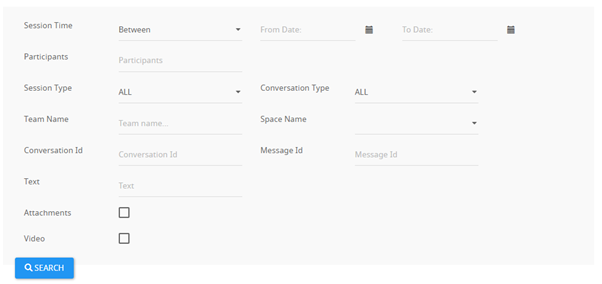
AGAT’s eDiscovery can be fully integrated with their DLP functionalities to avoid sensitive data being sent by text, files or even oral conversations
Conclusion
While many traditional archiving solutions fall short when addressing the needs of US companies having EU presence, AGAT steps in bringing an all encompassing on-premise solution that avoids the hefty fines of GDPR breaches.
Contact Us today to see how our innovative solution can streamline your data archiving process and ensure compliance with both US regulations and GDPR requirements.